项目代码:build_and_train_rnn
1 循环神经网络模型 RNN
循环神经网络(RNN)是一种神经网络类型,其神经元的输出在下一个时间步会反馈作为输入,使网络具有处理序列数据的能力。
RNN 能够处理变长序列,擅长挖掘数据中的时序信息。但是存在长期以来问题,难以处理长序列中相距较远的信息关联。RNN与普通神经网络的主要区别在于其具有记忆功能,神经元的输出能作为下一步输入,可处理序列数据,且输入和输出长度不固定。
在传统的前馈神经网络(Feedforward Neural Network)中,数据是从输入层流向输出层的,而在 RNN 中,数据不仅沿着网络层级流动,还会在每个时间步骤上传播到当前的隐层状态,从而将之前的信息传递到下一个时间步骤。
隐状态(hidden state):RNN 通过隐状态来记住序列中的信息。隐状态通过上一时间步的隐状态和当前输入共同计算得到。
RNN 在自然语言处理方面,可用于语言模型来预测下一个单词的概率,还能完成机器翻译、文本生成任务;在语音识别领域,能够处理语音这种时间序列信号,提高识别准确率;在时间序列预测中,像股票价格预测、天气预测等,RNN 通过学习历史数据模式预测未来值;在视频分析中,可以处理视频帧序列,进行动作识别等操作。
RNN 网络结构图:
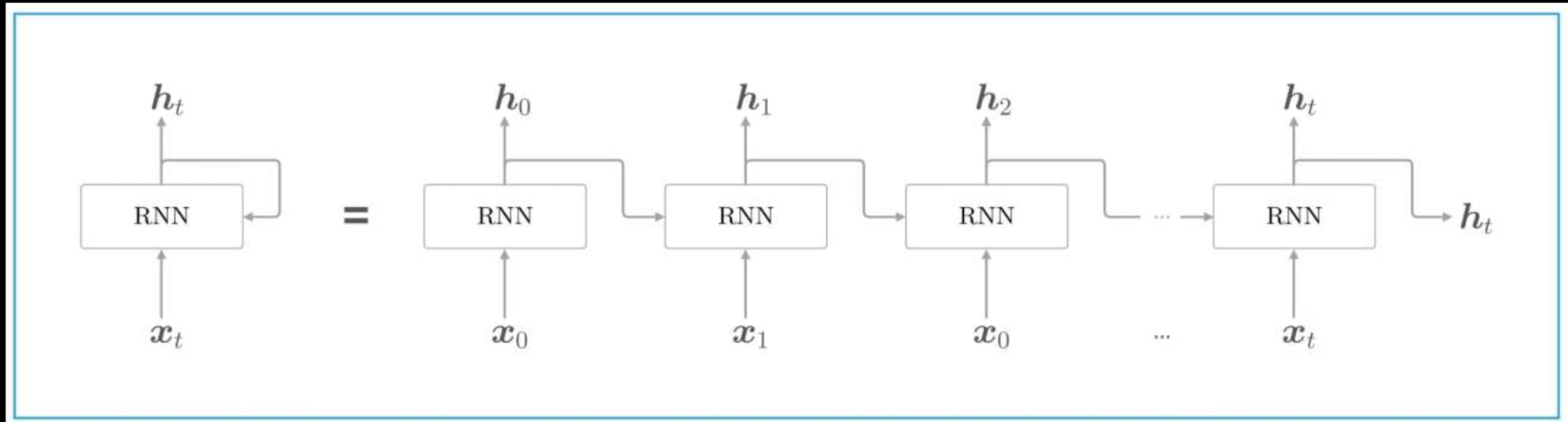
RNN 公式:
\[[h_t = f (h_{t-1}W_{hh} + x_tW_{xh} + b_h)]\]注:
- $h_t$:当前时刻的隐状态
- $h_{t-s}$:前一时刻的隐状态
- $x_t$:当前时刻的输入
- $W_{hh}, W_{xh}$:权重矩阵
- $b$:偏置项
- $f$:激活函数,例如 tanh,ReLU
输出(Output):RNN 的输出不仅依赖当前的输入,还依赖于隐状态的历史信息
公式:
\[y_t = W_{hy} h_t + b_y\]- $y_t$:在时间步 t 的输出向量(可选,取决于具体任务)。
- $W_{hy}$:是隐藏状态到输出的权重矩阵
2 RNN 处理序列数据的过程
循环神经网络(RNN)在处理序列数据时的展开(unfold)视图如下:
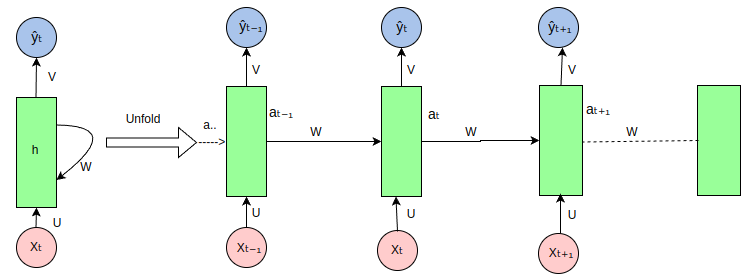
RNN 是一种处理序列数据的神经网络,通过循环连接来处理序列中的每个元素,并在每个时间步传递信息,以下是图中各部分的说明:
-
输入序列
(Xt, Xt-1, Xt+1, ...):图中的粉色圆圈代表输入序列中的各个元素,如Xt表示当前时间步的输入,Xt-1表示前一个时间步的输入,以此类推。 -
隐藏状态
(ht, ht-1, ht+1, ...):绿色矩形代表 RNN 的隐藏状态,它在每个时间步存储有关序列的信息。ht是当前时间步的隐藏状态,ht-1是前一个时间步的隐藏状态。 - 权重矩阵(U, W, V):
U:输入到隐藏状态的权重矩阵,用于将输入Xt转换为隐藏状态的一部分。W:隐藏状态到隐藏状态的权重矩阵,用于将前一时间步的隐藏状态ht-1转换为当前时间步隐藏状态的一部分。V:隐藏状态到输出的权重矩阵,用于将隐藏状态ht转换为输出Yt。
-
输出序列
(Yt, Yt-1, Yt+1, ...):蓝色圆圈代表 RNN 在每个时间步的输出,如Yt是当前时间步的输出。 -
循环连接:RNN 的特点是隐藏状态的循环连接,这允许网络在处理当前时间步的输入时考虑到之前时间步的信息。
-
展开(Unfold):图中展示了 RNN 在序列上的展开过程,这有助于理解 RNN 如何在时间上处理序列数据。在实际的 RNN 实现中,这些步骤是并行处理的,但在概念上,我们可以将其展开来理解信息是如何流动的。
- 信息流动:信息从输入序列通过权重矩阵
U传递到隐藏状态,然后通过权重矩阵W在时间步之间传递,最后通过权重矩阵V从隐藏状态传递到输出序列。
3 构建 RNN 网络
3.1 基于torch.nn.RNN构建 RNN 网络
在 PyTorch 中,RNN 可以用于构建复杂的序列模型。
PyTorch 提供了几种 RNN 模块,包括:
torch.nn.RNN:基本的 RNN 单元。torch.nn.LSTM:长短期记忆单元,能够学习长期依赖关系。torch.nn.GRU:门控循环单元,是 LSTM 的简化版本,但通常更容易训练。
使用 RNN 类时,需要指定输入的维度、隐藏层的维度以及其他一些超参数。
使用 pytorch 的torch.nn.RNN来构建 RNN 网络:
class SimpleRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(SimpleRNN, self).__init__()
# 定义 RNN 层
# batch_first=True表示输入数据的维度为[batch_size, seq_len, input_szie]
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
"""
多种单层的 RNN 层
单向、单层rnn, 1个时间步
single_rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=4, hidden_size=3, num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 4) # 输入数据维度为[batch_size, time_steps_num, input_size], time_steps_num 实际上就是 input sequence length
output, h_n = single_rnn(input) # output维度为[batch_size, time_steps_num, hidden_size=3],h_n维度为[num_layers=1, batch_size, hidden_size=3]
单向、单层rnn, 2个时间步
single_rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=4, hidden_size=3, num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
input = torch.randn(1, 2, 4) # 输入数据维度为[batch_size, time_steps_num, input_size]
output, h_n = single_rnn(input) # output维度为[batch_size, time_steps_num, hidden_size=3],h_n维度为[num_layers=1, batch_size, hidden_size=3]
双向、单层rnn
bi_rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=4, hidden_size=3, num_layers=1, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
bi_output, bi_h_n = bi_rnn(input)
"""
# 定义全连接层
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
# x: (batch_size, seq_len, input_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(x) # out: (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)
# 取序列最后一个时间步的输出作为模型的输出
out = out[:, -1, :] # (batch_size, hidden_size)
out = self.fc(out) # 全连接层
return out
3.2 基于 pytorch 手搓 RNN
激活函数使用 $\tanh$,那么 RNN 的公式变成:
\[[h_t = \tanh (h_{t-1}W_{hh} + x_tW_{xh} + b_h)]\]class RNNLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers=1, batch_first=True):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.input_size = input_size
self.bidirectional = False
self.W_hh = nn.Parmater(torch.rand(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size))
self.W_ih = nn.Parmater(torch.rand(self.input_size, self.hidden_size))
self.b_ih = nn.Parmater(torch.zeros(self.hidden_size))
self.b_hh = nn.Parmater(torch.zeros(self.hidden_size))
def forward(self, x_t, h_prev=None):
"""
1: torch.matmul(x_t, self.W_ih)
x_t包含多个时间步,形状为[batch_size, time_steps_num, input_size] # input_size 实际上就是 input 的维度 input_dim
W_ih形状为[input_size, hidden_size]
torch.matmul(x_t, self.W_ih) 输出矩阵形状为[batch_size, time_steps_num, hidden_size]
2: torch.matmul(h_prev, self.W_hh)
h_prev 形状为[batch_size, time_steps_num, hidden_size]
W_hh形状为[hidden_size, hidden_size]
torch.matmul(h_prev, self.W_hh) 输出矩阵形状为[batch_size, time_steps_num, hidden_size]
"""
if h_prev == None:
h_prev = torch.zeros( x_t.size(0), self.hidden_size)
output = torch.matmul(x_t, self.W_ih) + self.W_ih + torch.matmul(h_prev, self.W_hh) + self.b_hh
output = torch.tanh(output)
return output, output[:, -1, :].unsqueeze(0)
4 训练并测试模型
4.1 创建数据集
为了训练 RNN,我们生成一些随机的序列数据。这里的目标是将每个序列的最后一个值作为分类的目标。
# 生成一些随机序列数据
num_samples = 100000
seq_len = 100
input_size = 10
output_size = 2 # 假设二分类问题
# 随机生成输入数据 (batch_size, seq_len, input_size)
X = torch.randn(num_samples, seq_len, input_size)
# 随机生成目标标签 (batch_size, output_size)
Y = torch.randint(0, output_size, (num_samples,))
# 创建数据加载器
dataset = TensorDataset(X, Y)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
4.2 定义损失函数与优化器
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 多分类交叉熵损失
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
4.3 训练模型
num_epochs = 25
model.train() # 设置模型为训练模式
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
total_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
for inputs, labels in train_loader:
# 前向传播
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# loss
total_loss += loss.item()
# 计算准确率
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
accuracy = 100 * correct / total
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {total_loss / len(train_loader):.4f}, Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}%")
4.4 测试模型
model.eval() # 设置模型为评估模式
with torch.no_grad():
total = 0
correct = 0
for inputs, labels in train_loader:
outputs = model(inputs)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
accuracy = 100 * correct / total
print(f"Test Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}%")
4.5 模型训练评估完整代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from modeling_rnn_torch_nn_rnn import SimpleRNN
from modeling_rnn_craft import CustomRNN
def plot_loss(loss, pic_path = './loss_curve.png'):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(
loss,
color='red',
linestyle='-',
# marker='o',
linewidth=1,
label='Training Loss'
)
plt.ylim(0, max(loss)*1.1)
plt.xlabel('epoch_num', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('loss', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Loss Curve', fontsize=14)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)
plt.legend()
plt.savefig(pic_path)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 数据集:字符序列预测(Hello -> Elloh)
char_set = list("hello")
char_to_idx = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(char_set)}
idx_to_char = {i: c for i, c in enumerate(char_set)}
input_str = "hello"
target_str = "elloh"
input_data = [char_to_idx[c] for c in input_str]
target_data = [char_to_idx[c] for c in target_str]
# 转换为独热编码
input_one_hot = np.eye(len(char_set))[input_data]
# 转换为 PyTorch Tensor
inputs = torch.tensor(input_one_hot, dtype=torch.float32)
targets = torch.tensor(target_data, dtype=torch.long)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 超参
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
input_size = len(char_set)
hidden_size = 8
output_size = len(char_set)
num_epochs = 1000
learning_rate = 0.01
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# train and eval
def train_model(model, model_type = "craft", inputs = None, targets = None):
print(f"\nTrain on {device}\n")
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if not param.requires_grad:
print(f"⚠️ 参数未启用梯度: {name}")
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
losses = []
hidden_state = None
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播
if model_type == "craft":
outputs = []
for index in range(inputs.shape[0]):
output, hidden_state = model(inputs[index], hidden_state)
hidden_state = hidden_state.detach() # 防止梯度爆炸
outputs.append(output)
outputs = torch.stack(outputs, dim=0).squeeze(1)
else:
outputs = None
for index in range(inputs.shape[0]):
output, hidden_state = model(inputs.unsqueeze(0), hidden_state)
hidden_state = hidden_state.detach() # 防止梯度爆炸
outputs = torch.cat((outputs, output), dim=0) if outputs is not None else output
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
losses.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print(f"Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}")
# 测试
with torch.no_grad():
test_hidden = None
if model_type == "craft":
predicts = []
for index in range(inputs.shape[0]):
test_output, _ = model(inputs[index].unsqueeze(0), test_hidden)
if device != "cpu":
predicted = torch.argmax(test_output, dim=1).item()
else:
predicted = torch.argmax(test_output, dim=1)
predicts.append(predicted)
print("Input sequence: ", ''.join([idx_to_char[i] for i in input_data]))
print("Predicted sequence: ", ''.join([idx_to_char[i] for i in predicts]))
print("Target sequence: ", target_str)
else:
test_output, _ = model(inputs.unsqueeze(0), hidden_state)
if device != "cpu":
predicts = torch.argmax(test_output, dim=1).cpu().squeeze().numpy()
else:
predicts = torch.argmax(test_output, dim=1).squeeze().numpy()
plot_loss(losses, f"loss_curve_{model_type}.png")
if __name__ == "__main__":
model_craft = CustomRNN(input_size, hidden_size, output_size).to(device)
model_torch_rnn = SimpleRNN(input_size, hidden_size, output_size).to(device)
train_model(model_craft, "craft", inputs = inputs.to(device), targets = targets.to(device))
train_model(model_torch_rnn, "torch_rnn", inputs = inputs.to(device), targets = targets.to(device))
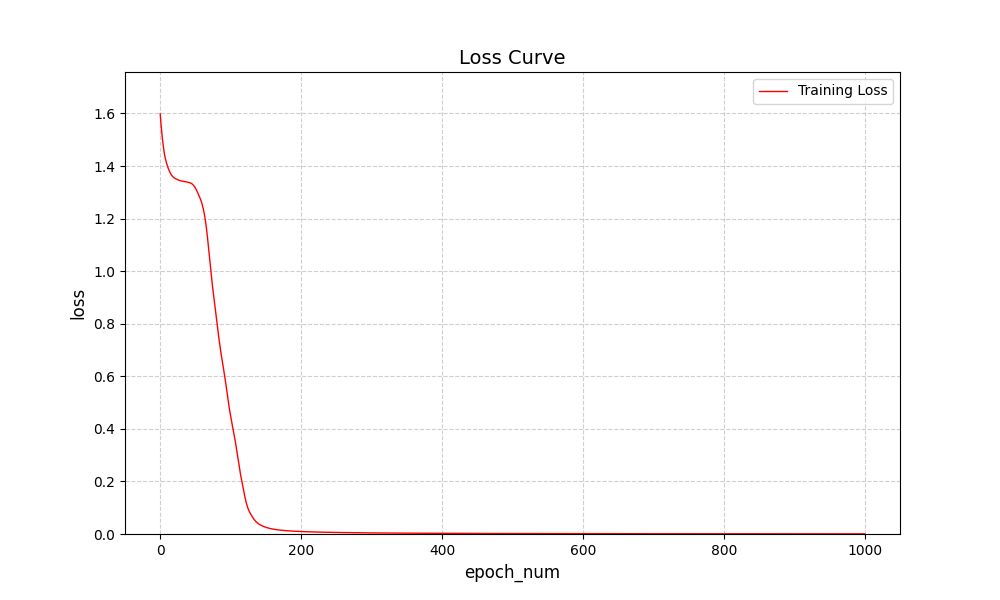
网络比较简单,收敛的很快:
Reference:
- hack-rnns
-
[PyTorch 循环神经网络(RNN) 菜鸟教程](https://www.runoob.com/pytorch/pytorch-recurrent-neural-network.html)